Causes of Hip Pain
Hips are the largest ball-and-socket joint, designed to support the weight of the entire body. When hips are affected with a painful condition, it can be debilitating.
Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic hip pain. Hip pain may also occur from overuse injuries in which muscles, tendons, and ligaments can become inflamed. These injuries may be due to routine daily activities or one specific event.
There are many different types of hip injuries; however, there are a few that are more common than others. Common types of hip injuries include tendonitis, bursitis, contusions and sprains. These conditions can cause hip pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Two common causes of hip pain involve arthritis of the hip or hip injuries:
Common Types of Arthritis of the Hip:
Common Types of Hip Injuries:
Diagnosing Hip Pain
Your orthopedic surgeon will evaluate your health history, perform a physical examination, and take x-rays to diagnose your hip pain.
- Medical history
- Symptoms
- Health
- Activity
- Examine affected joint
- Range of motion tests
- Joint-line tenderness
- Joint deformities
- X-rays
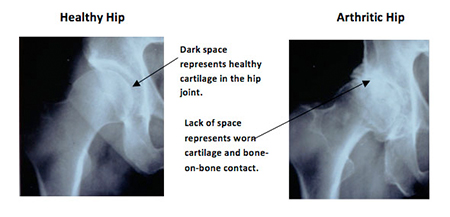
An x-ray will help your surgeon diagnose your hip pain. On an x-ray, a healthy hip joint appears as if there is a space between the bones in the joint. Although you cannot see the cartilage on an x-ray, in the healthy hip, the cartilage is working to cushion and smooth the movement of the thighbone (femur) against the hip socket (acetabulum). On the x-ray of a hip with osteoarthritis, there is bone on bone contact because the cartilage between the femur and acetabulum has been worn away.
When non-surgical treatments such as diet, exercise, medications, supplements, and physical therapy fail, your orthopedic surgeon may recommend total hip replacement.
You should discuss your condition and treatment options with your surgeon.
All patient education materials are provided by OrthoPatientEd.com and have been reviewed by our Advisory Board of leading Orthopedic Surgeons to ensure accuracy. All materials are provided for informational purposes only and are not intended to be a substitute for medical advice from your orthopedic surgeon. Any medical decisions should be made after consulting a qualified physician.
This site includes links to other websites. OrthoPatientEd.com takes no responsibility for the content or information contained in the linked sites.
